Effectiveness of Integrated Teaching Among First MBBS Students
Abstract
Introduction
The arrangement of teaching content to relate to or unite concepts that are regularly taught in different academic courses or departments is referred to as integration of teaching. It simply refers to creating links between theoretical knowledge and actual application. Teaching the fundamental sciences in separate blocks prevents students from having the opportunity to connect and integrate their newly acquired knowledge.
Objectives
To evaluate the effectiveness of Integrated teaching method over traditional teaching and perception of students towards integrated method among first MBBS students
Methodology
The total of 62MBBS first year students are randomly divided into two groups, with 31 in each group. Group A is subjected for Conventional teaching and Group B for Integrated teaching method in the same topic. Among the 2 sessions one session is Horizontal and other is Vertical method of integrated teaching have been implemented. Finally, an evaluation test was conducted for both the groups and the mean marks obtained by the students were analyzed by using SPSS software version 17. Student’s perception towards this method was evaluated by pre-validated feedback questionnaire and analyzed.
Results
The mean marks (outof40) obtained by Group B (Conventional teaching) is 13.82 and by Group A (Integrated Teaching) is 31.18. So, the marks obtained by students after integrated method were found to be higher than the other group which underwent conventional teaching and this difference was found to be statistically significant (P <0.0001).
Discussion and conclusion
In comparison to the typical conventional method, integrated teaching has been found to be a more successful mode of instruction in terms of students' performance and assessment exams.
Author Contributions
Academic Editor: Karunamoorthy Jayamoorthy, Department of chemistry St. Joseph's College of Engineering.
Checked for plagiarism: Yes
Review by: Single-blind
Copyright © 2024 Supriya Garapati, et al
 This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Citation:
Introduction
"Education that is designed in such a way that it cuts across subject matter lines, bringing together many components of the curriculum into meaningful association to focus upon broad areas of study," according to Shoemaker et al., is what is meant by an integrated curriculum 1. Since Flexner's time, medical education has tended to emphasize basic sciences before clinical sciences, although this is not how patients are presented today. This strategy is frequently criticized on the grounds that students will not be able to understand how to relate the basic sciences with clinical practice . It is desirable to encourage students to think like doctors as soon as they enroll in medical school 1, 2.
Since basic science learning is placed in the context of clinical and professional practice and is viewed by students as being more meaningful and relevant, integration is crucial for medical education. Can add what is horizontal integration. Vertical integration mixes basic and clinical sciences with early clinical experience in the vast majority of curriculum revisions, and this is unquestionably a benefit and a resurrection in medical education 1, 2.
The arrangement of teaching content to relate or converge the subjects that are regularly taught in different academic departments or courses is known as integration of teaching 3. The benefits of integrated teaching over traditional lectures include reducing the fragmentation of medical courses, avoiding repetition and time waste, and teaching students to apply their knowledge to clinical practice. It also encourages interdepartmental collaboration and the rationalization of teaching resources 4. When comparing student performance on assessment exams, integrated teaching outperforms traditional instruction 5. The drawbacks include a lack of cooperation, more effort required to organize the integrated session, a lack of institutional infrastructure, a lack of time and dedication, and a lack of interdepartmental coordination. When integrated instruction is offered, integrated assessment should also be taken into account 3, 4, 5.
Objectives
1. To evaluate the effectiveness of Integrated teaching method over traditional teaching among 1st MBBS students by Questionnaire
2. To evaluate the student perception towards integrated teaching
Methodology
The study was carried out after obtaining approval and clearance from the Institute Research Cell and the Institute Ethics Committee (IEC: AIIMS/BBN/IEC. Feb/2021/06a/24.02.2021). The study was carried out among the first year M.B.B.S. students in AIIMS Bibinagar. The study participation was voluntary. We provided all students with detailed information about the study's objectives and assured them of confidentiality and anonymity when it came to their personal information.
Study participants
The study involved a total of 62 participants (38 male and 24 female). The sample size of 62 was calculated based on feasibility and with references from previous studies. The participants were divided into 2 groups (Group A – control group) and (Group B- interventional group), each consisting of 31 participants.
Methods
Participants from Group A were given conventional didactic lectures separately as per the schedule in their respective departments for 3 months – Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry. Participants from Group B underwent integrated teaching for 3 months for the same topics as per the schedule – horizontal integration and vertical integration, depending upon the topics covered. For example, for topics such as muscular dystrophies, horizontal integration was done between the first year departments – Anatomy, Physiology and Biochemistry for a period of 3 hours. For topics such as thyroid gland, vertical integration was done between Anatomy and Surgery departments.
Appropriate statistical analysis was done using SPSS software (SPSS version 17). After each integrated session, pre test and post test was taken for the participants and compared using paired t test and p value < 0.01was considered statistically significant. The mean total score was also compared between both the groups and p value < 0.01was considered statistically significant.
A pre validated questionnaire for feedback comprising both closed ended and open ended questions prepared on the basis of 5 point Likert scale were used to assess the learning experience of the students in the interventional group and their perception towards the activity.
Results
There was a significant difference in the performance of students after the teaching sessions. Integrated session post test scores were found to be better than conventional teaching method scores in both the sessions (Table 1 and Table 2).
Table 1. Horizontal Integrated session- Comparison of scores obtained by students in pre- and post-test| Scores obtained (for 15 marks) | Mean | S. D | P value |
| Pre-test | 10 | 3 | < 0.001 |
| Post-test | 14 | 2 |
| Scores obtained (for 10 marks) | Mean | S.D | P value |
| Pre-test | 6 | 2 | < 0.04 |
| Post-test | 10 | 0 |
The below Table 3 shows that mean ranks of integrated teaching is higher than the conventional one and the difference between them was found to be statistically significant.
Table 3. Mean ranks of Integrated teaching Vs Conventional teaching| Type of teaching | Mean rank | P value |
| Conventional | 13.82 | < 0.04 |
| Integrated | 31.18 |
Discussion
The concept of this study stems with the idea of alignment and integration of medical education curriculum that is well represented in the below diagram (Figure 1). Integration of medical curriculum consists of sharing the knowledge concept with other peers, correlating it with the Previously known related concepts and nesting them within one’s mind for a thorough rehearsal 6, 7. A temporal co-ordination also exists between aligning the learnt concepts with newly acquired integrated concepts (illustrated in Figure 1).
Figure 1.Relationship between alignment and integration in curriculum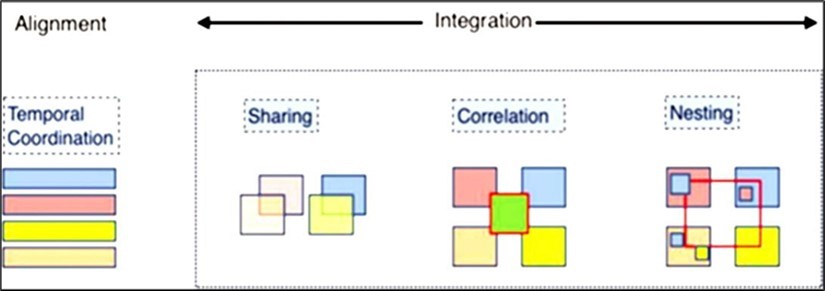
(Courtesy-Patel M, Shah HD. Alignment and integration in competency-based medical education curriculum:An overview. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2020;64(Suppl_1): S13-S5.)
The inverted triangle model of integrated teaching plays a key role in medical curriculum (Figure 2), wherein an equal distribution of grasped knowledge exists between the clinical, para-clinical and pre-clinical subjects that are mirror images of each other (Figure 2) 8, 9.
Figure 2.Inverted triangle model of Integrated teaching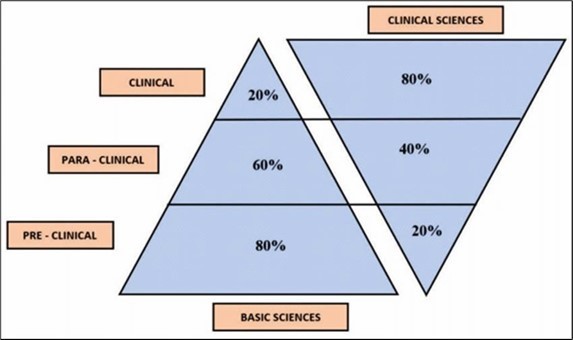
( Courtesy- Journal of Research in Medical Education & Ethics Vol. 9, No. 3, November, 2019, pp-165-173)
TYPES OF INTEGRATED TEACHING The most common types of integrated teaching in the context of medical education are:
Horizontal Integration - It is organizing of topic across disciplines over a set amount of time. It involves combining two or more subjects that are covered in the same curriculum phase. In other words, horizontal integration refers to the merging of the educational identities of two or more departments that are concurrently teaching 15
Vertical Integration - Organization of subject knowledge across disciplines over an in definite duration. Integrating two or more disciplines taught during various phases of the curriculum. In other words, vertical integration is an integration between disciplines traditionally taught in the different phases of curriculum 15.
The spiral approach to integrated curriculum (Figure 3) divides the attitudes, cognitions and skills into three processes that are inter-related with each other 9, 10.
Figure 3.Spiral approach towards integrated curriculum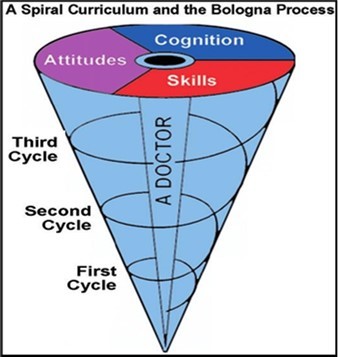
(Courtesy- Madelena Patritio & Ronald, The Bologna Process - A global vision for the future of medical education: MedicalTeacher 32(4):305-15
The results of our study show that the students are well acquainted after the post test scores in both the types of integration and their mean ranks are also higher in vertical integration. This indirectly shows their positive attitude towards integrated curriculum. These results of ours are partially consistent with those of Priyanka A et al 10 who had shown in their study that 12%students from integrated teaching group scored more than 80% marks whereas 8.95% students from didactic lecture group scored more than 80% marks. 71% students from group A scored 60-80% marks in comparison to Group B where 45% students scored 60-80% marks 10.In group A of their study, 11% students scored 50-60% marks and 4.7% students scored less than 50%marks. In group B, 23.88% students scored 50-60% marks and 14.92% students scored less than50% marks 10. Similar studies at Seth GS Medical College, Mumbai, Maharasthra by Joglekaretal at MGM's Medical College, Navi Mumbai, India by Kateetal 6 at Pramukh swami Medical College, Karamsad, Gujarat by Ghosh and Pandya 8 at Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Belgaum Karnataka by Dandannavar and at Terna Medical College, Nerul, Navi Mumbai by Nikam and Chopade 8, 9 revealed that the marks obtained by the students who had undergone integrated teaching was statistically and significantly greater than those who did not1, 8, 9, 10.
A systematic approach towards teaching and learning methodologies has always increased the enthusiasm and motivation among students for better grasping of the subjects as shown in previous studies 11, 12. The use of pre tests and post tests not only helps to evaluate their knowledge but also helps them stay focused on the subject as they are aware that an objective assessment awaits them at the end of the session(12,13). Studies have also shown that such integrated learning methods among students help them retain concepts for a long term basis in a student friendly way 13, 14
Conclusion
The integrated teaching was found to be a better effective tool of teaching than the traditional conventional method in terms of students' performance in assessment examinations.
References
- 1.Shoemaker B J E. (1989) Integrative Education: A Curriculum for the Twenty-First Century. OSSC Bulletin. 33(2): n2. [Google Scholar]
- 2.R M Harden. (1986) Approaches to curriculum planning. Med Educ. [PubMed] [Google Scholar] 20(5), 458-466.
- 3.Basu M, Das P, Chowdhury G. (2015) Introducing integrated teaching and comparison with traditional teaching in undergraduate medical curriculum: A pilot study. , Med J DY Patil Univ 8(4), 431-8.
- 5.Doraisamy Ravichandran. (2013) Shankar Radhakrishnan The effectiveness of integrated teaching over traditional teaching among first MBBS students: A preliminary study year. 6, 139-141.
- 6.Brauer D G, Ferguson K J. (2014) The integrated curriculum in medical education:. AMEE Guide No.96. Med Teach. 2015 Apr;37(4): 312-22. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2014.970998. Epub 25319403.
- 7.Bandiera G, Boucher A, Neville A, Kuper A, Hodges B. (2013) Integration and timing of basic and clinical sciences education. Med Teach. May;35(5): 381-7. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2013.769674. Epub 23444888.
- 8.Spencer A L, Brosenitsch T, Levine A S, Kanter S L. (2008) Back to the basic sciences: an innovative approach to teaching senior medical students how best to integrate basic science and clinical medicine. Acad Med. 83(7), 662-9.
- 9.Eisenstein A, Vaisman L, Johnston-Cox H, Gallan A, Shaffer K et al. (2014) Integration of basic science and clinical medicine: the innovative approach of the cadaver biopsy project at the Boston University School of Medicine. Acad Med. 89(1), 50-53.
- 11.Estai M, Bunt S. (2016) Best teaching practices in anatomy education: A critical review. Ann Anat. Nov;208: 151-157. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2016.02.010. Epub 6996541.
- 12.Eppler E, Serowy S, Link K, Filgueira L. (2018) Experience from an optional dissection course in a clinically-orientated concept to complement system-based anatomy in a reformed curriculum. Anat Sci Educ. Jan;11(1): 32-43. doi: 10.1002/ase.1707. Epub 28608954.
- 13.Han E R, Yeo S, Kim M J, Lee Y H, Park K H et al. (2019) Medical education trends for future physicians in the era of advanced technology and artificial intelligence: an integrative review. BMC Med Educ. 19(1), 460-10.
